A Retailer’s Technical Guide to AI Agents in Merchandising
In the hyper-competitive retail industry, the most critical decisions are often made long before a customer clicks “add to cart” or walks into a store and finds an article to purchase.
These are the merchandising decisions: what to stock, how much to stock, how to display it, and how to price it.
For decades, this has been a delicate dance of historical analysis, market intuition, and educated guesswork. Today, AI and retail are converging to transform this art into a science, creating a formidable competitive advantage for those who adopt it. And for those who don’t, this becomes a serious disadvantage.
So, how do retail leaders and practitioners move beyond the buzzwords and understand the practical mechanics of AI in retail for merchandising?
Let us dissect how Retail AI solutions are revolutionizing demand forecasting, pricing strategies, and product assortment to maximize revenue and profit and how AI Agents can be used to recover potentially lost revenue.
According to a report by Harvard Business Review, retailers lose nearly $1 trillion annually due to a combination of overstocks and stockouts. [1]
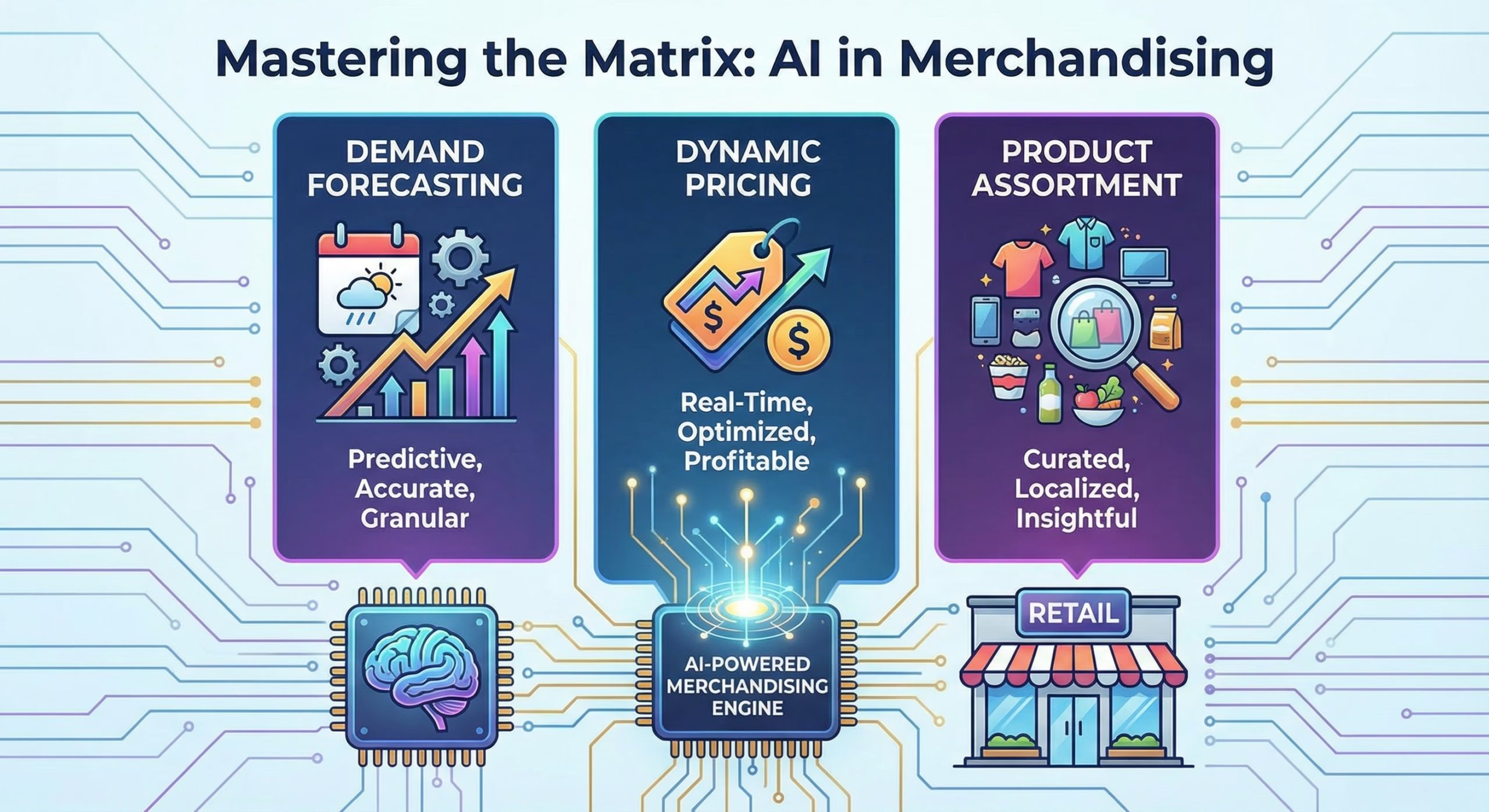
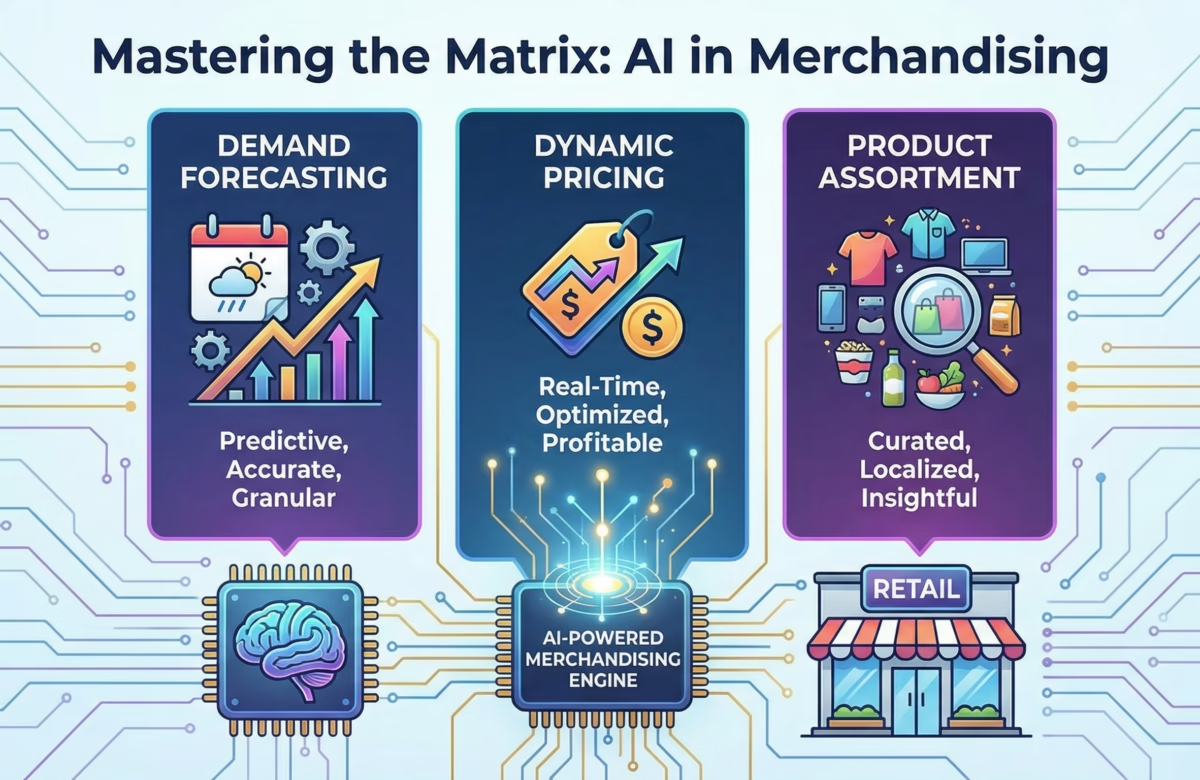
AI Agents for Merchandising Automation
Sophisticated AI models can provide the predictive and analytical power to transform merchandising. But they leave the execution to a human to do manually. The insights generated by these models still require manual intervention from merchandisers and analysts to implement, monitor, and report on. The next evolution of Retail AI solutions is AI Agents.
AI Agents are autonomous, digital team members working alongside human experts. Agents are designed to execute the routine, mechanical tasks that surround the core AI models, freeing up the team to focus on high-level strategy, creative direction, and exception handling. These agents act on the data and insights, turning analysis into action, 24x7x365.
AI Powered Demand Forecasting: From Actionable to Actioned
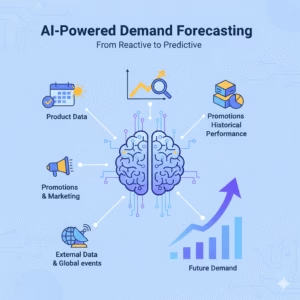
The most fundamental challenge in merchandising is not just accurately predicting future demand, but also executing on this information. Traditional prediction methods, often based on simple moving averages or year-over-year comparisons, are no longer sufficient in a market influenced by fast-changing trends, social media, and complex global events.
How it Works: Modern AI retail solutions leverage sophisticated machine learning models, such as Time-Series Forecasting (e.g., ARIMA, Prophet) and Regression models (e.g., XGBoost, Random Forest). These models go far beyond historical sales data, integrating a wide array of features to build a holistic predictive view, including Product Data such as style, color, size. Historical Performance such as Sales velocity, returns data, causal factors: Promotions, marketing campaigns, External Data: Competitor pricing, macroeconomic indicators.
By analysing the complex, non-linear relationships between these variables, the AI can produce granular forecasts at the SKU, store level – daily, weekly, seasonally or as needed. This allows for a shift from a reactive inventory strategy to a predictive one – creating actionable insights.
While this predictive data is actionable, it still needs manual intervention to execute on the recommendations. AI Agents use the predictive models as tools to understand the outcomes, check if the data allows decisioning, take a decision and then execute with human supervision.
The Technical Edge of AI in Practice:
| Traditional Method | AI-Powered Method |
| Relies on last year’s sales for a similar period. | Analyzes hundreds of variables, identifying that a heatwave forecast (external data) will boost demand for specific summer apparel (product data) even if last year was unseasonably cool. |
| A flat 10% uplift is applied for a planned promotion. | The model predicts a variable uplift based on the specific discount, channel, and customer segment, suggesting a 15% discount is optimal for maximizing margin. |
| Manual intervention to execute the actions across all products, regions, etc. | AI Agent executes forecasting, monitors results, executes the actions needed, with human-in-the-loop monitoring. |
Actioning Algorithmic Pricing and Promotion Optimization

Pricing is a powerful profit lever, yet many retailers still rely on static, cost-plus, or competitor-matching strategies. Artificial intelligence in retail enables a dynamic, data-driven approach that optimizes pricing for every product, in every channel, at every moment.
How it Works: AI-driven pricing engines use reinforcement learning and price elasticity models to understand how demand for a product changes at different price points. The goal is to find the optimal price that maximizes revenue or profit, depending on the business objective.
The system constantly ingests and analyses data streams, including:
- Real-time demand signals (e.g., conversion rates, add-to-cart velocity).
- Inventory levels (e.g., automatically applying markdowns for slow-moving items).
- Competitor pricing data
- Customer segmentation data
This allows for automated, intelligent pricing decisions. For example, the price of a popular item might be slightly increased during peak demand, while a product with high inventory and an approaching expiration date is automatically marked down to clear stock and recover value.
Static pricing leaves money on the table. Our philosophy is that every product has an optimal price, and our AI solutions are designed to find it. Agents can suggest prices and can execute on small fluctuations, but only humans can approve major changes.
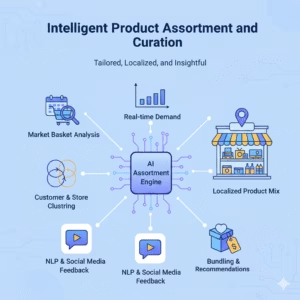
Intelligent Product Assortment and Curation
What products should a retail store carry in the first place? And how should the assortment differ between a downtown flagship store and a suburban mall location? What is the preference of purchasers in one location, and how does it differ from another?
AI can provide insights and answers. AI Agents can execute on the insights.
How it Works: By applying techniques like market basket analysis and affinity analysis to customer transaction data, AI can uncover hidden purchasing patterns. This reveals which products are frequently bought together, allowing for smarter product bundling and cross-selling recommendations.
Furthermore, by clustering customer data with geographic and demographic information, AI can help retailers tailor their product assortments to local tastes and preferences. This moves beyond a one-size-fits-all approach to create a highly relevant and localized shopping experience. Local events, customs and other influences can be taken into account to create per-store product assortments, and display options.
Key AI techniques include:
- Clustering Algorithms (e.g., K-Means): To group stores or customer segments with similar purchasing behaviors.
- Association Rule Mining (e.g., Apriori algorithm): The relationships between events can be used to identify “if-then” patterns, such as “If a customer buys product X, they are 80% likely to also buy product Y.”
These agents can scan product reviews to provide real-time insights into customer desires.
This provides merchandisers with a direct, data-driven feed of assortment opportunities, reducing the reliance on manual research and intuition.
These inputs can then be used to automatically understand the best assortment for the retail store to use.
The Agentic Merchandising of Tomorrow is Here Today
Embracing AI in retail merchandising is no longer an optional innovation; it is a foundational requirement for survival and growth. By leveraging these powerful AI retail solutions, retailers can move from a reactive to a predictive posture, making smarter, faster, and more profitable decisions.
Here are some common manual merchandising tasks and how dedicated AI Agents can automate them:
The journey begins with a commitment to data quality and a willingness to trust algorithmic insights and AI Agents. These Agents must be built, tested, monitored, and run using Responsible AI principles. The retailers who master this new Agentic AI merchandising matrix will be the undisputed leaders of the next generation of commerce.
References
[1] https://hbr.org/2024/10/how-online-retailers-can-avoid-costly-out-of-stock-issues